Image credit: NVIDIA
AI is making a big difference for all kinds of people—from researchers finding new drugs to analysts keeping up with financial markets. The quicker an AI system can generate tokens (small chunks of data that build its outputs), the bigger its impact. That’s where AI factories come in—they’re the fastest way to go from that first token to delivering real value. These factories are shaking up the economics of modern tech by turning data into useful stuff like predictions, images, or proteins on a massive scale.
They boost three key parts of the AI process: taking in data, training models, and handling lots of requests. AI factories are designed to create tokens faster and more accurately using three main tech building blocks: AI models, speedy computing power, and reliable software. Keep reading to see how these factories are helping businesses and organizations worldwide turn data—their most valuable asset—into money-making opportunities!
From Understanding Costs to Creating Value
Before setting up an AI factory, it’s smart to get a handle on inference economics—how to balance costs, energy use, and growing AI demand. Throughput is about how many tokens a model can produce, while latency measures how fast it delivers them—starting with the time to the first token and then each one after. There’s also a newer term, goodput, which tracks how much useful output you get while meeting latency goals.
User experience is a big deal for any app, and AI factories are no different. High throughput means smarter AI, and low latency keeps responses quick. When these are balanced right, you get a great experience—like an AI customer service agent answering in half a second versus five, even if both give the same answer. Companies can set competitive prices for these outputs, boosting revenue per token. Figuring out this balance can be tricky, and that’s where the Pareto frontier comes in handy.
AI Factory Output: Making Tokens Work
The Pareto frontier, shown in the figure below, helps you see the best ways to balance trade-offs—like fast responses versus serving more users at once—when scaling AI. The vertical axis shows throughput efficiency in tokens per second (TPS) per unit of energy, so a higher number means handling more requests at once. The horizontal axis shows TPS for a single user, which is how fast the first answer comes—higher is better for a smooth experience. Lower latency and quick responses are key for things like chatbots or real-time tools.

The top of the Pareto curve marks the best output for different setups. The goal is to find the sweet spot between throughput and user experience for various AI tasks. Top AI factories use fast computing to boost tokens per watt, improving performance and energy efficiency across the board. We’ve tested this: NVIDIA H100 GPUs run at 32 tokens per second per user, while NVIDIA B300 GPUs hit 344. At that level, Blackwell Ultra offers over 10 times better experience and nearly 5 times higher throughput, unlocking up to 50 times more revenue potential.
How an AI Factory Works in Real Life
An AI factory is a team of components that turns data into smart insights. It doesn’t have to be a fancy on-site data center—it could be a cloud setup, a hybrid model with fast computing, or even a telecom network that optimizes and runs AI at the edge. Basically, any dedicated fast computing setup paired with software to make data smart is an AI factory.
The pieces include fast computing, networking, software, storage, systems, and tools. When you ask an AI a question, the whole system kicks in. It breaks the prompt into tokens—small bits of meaning like parts of images or words—and sends them through a GPU-powered AI model for quick thinking. The GPUs work together using high-speed connections to process data at once. This happens for questions from users worldwide, creating intelligence on a huge scale in real time.
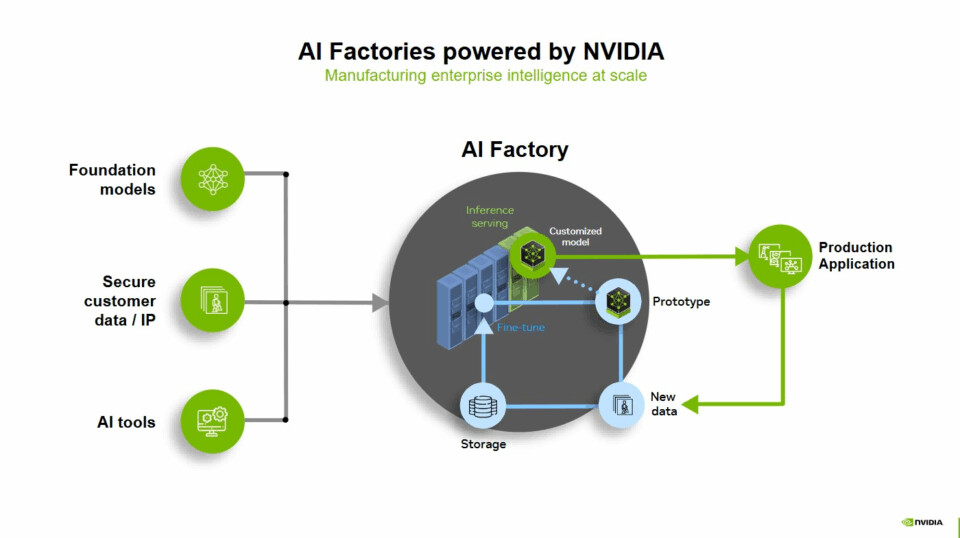
Since AI factories cover the whole AI lifecycle, they keep getting better. They log inference, flag tricky cases for retraining, and tighten optimization loops over time—all without needing hands-on help, showing goodput in action. Take Lockheed Martin, a leading security tech company, which built its own AI factory. Through its Lockheed Martin AI Center, they centralized their AI tasks on the NVIDIA DGX SuperPOD to train and tweak models, using specialized gear to cut cloud costs.
“With our on-site AI factory, we handle tokenization, training, and deployment ourselves,” said Greg Forrest, director of AI foundations at Lockheed Martin. “Our DGX SuperPOD processes over 1 billion tokens weekly, letting us fine-tune, enhance, or run inference on our large language models. This avoids the rising costs and limits of token-based fees.”
NVIDIA’s Full-Stack Tech for AI Factories
An AI factory turns AI from scattered experiments into a reliable, scalable engine for innovation and business growth. NVIDIA offers everything you need, like fast computing, high-performance GPUs, strong networking, and optimized software.
NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs, for instance, connect via networking, use liquid cooling for efficiency, and work with AI software. The NVIDIA Dynamo open-source platform acts like an operating system for AI factories, speeding up and scaling AI with low costs. It smartly routes and optimizes requests to keep every GPU busy, maximizing token output.
NVIDIA Blackwell GB200 NVL72 systems and InfiniBand networking boost token throughput per watt, balancing high output and low latency. By testing full-stack solutions, companies can build and maintain cutting-edge AI systems easily. This helps businesses achieve top performance, unlocking AI’s potential faster and with more confidence.
What do you think about these AI factories transforming how we use data? I’d love to hear your thoughts!
Source: NVIDIA Blog




